Difference between revisions of "NV2A/Vertex Shader"
(Added opcodes) |
(Add pipeline diagram) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
* Low-constants only / all constants | * Low-constants only / all constants | ||
* Vertex processing / State program | * Vertex processing / State program | ||
| + | |||
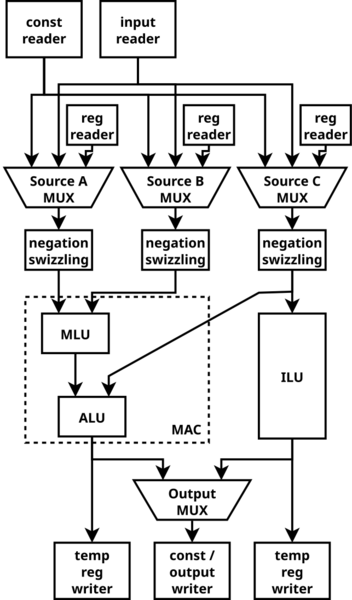
| + | == Pipeline == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Vertex_processor.png|352px]] | ||
== Registers == | == Registers == | ||
| Line 24: | Line 28: | ||
|+Output registers | |+Output registers | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | !Index | |
| − | + | !GL Name | |
| − | + | !D3D Name | |
| − | + | !Meaning | |
|- | |- | ||
|0 | |0 | ||
| Line 112: | Line 116: | ||
|+Fields | |+Fields | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | !Meaning | |
| − | + | !Word | |
| − | + | !Offset (bits) | |
| − | + | !Size (bits) | |
|- | |- | ||
|ILU Operation | |ILU Operation | ||
| Line 296: | Line 300: | ||
|+Swizzle table | |+Swizzle table | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | !Value | |
| − | + | !Meaning | |
|- | |- | ||
|0 | |0 | ||
| Line 320: | Line 324: | ||
|+ILU Operations | |+ILU Operations | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | !Value | |
| − | + | !Meaning | |
|- | |- | ||
|0 | |0 | ||
| Line 353: | Line 357: | ||
|+MAC Operations | |+MAC Operations | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | !Value | |
| − | + | !Meaning | |
|- | |- | ||
|0 | |0 | ||
| Line 398: | Line 402: | ||
|ARL | |ARL | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Related links == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * nvidia resources | ||
| + | ** [https://web.archive.org/web/20191214200729/https://www.nvidia.com/attach/6559 WhereIsThatVertexShaderInstruction.pdf] / [https://web.archive.org/web/20191214200738/https://www.nvidia.com/attach/6560 WhereIsThatVertexShaderInstruction.doc] | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/envytools/envytools/blob/master/nvhw/pgraph_celsius_xfrm.c Code which appears to implement bit-accurate emulation of some instructions]{{FIXME|reason=Unconfirmed, needs testing}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:NV2A]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:34, 19 December 2025
The Xbox implements the 2 GL extensions NV_vertex_program and NV_vertex_program1_1 (with some modifications). This article will mainly focus on actual encoding on hardware as the behaviour is mostly outlined in those GL extensions already.
Contents
Operating modes
- Fixed / Programmable
- Writeable / Read-Only constants
- Low-constants only / all constants
- Vertex processing / State program
Pipeline
Registers
Input registers
There are 16 input registers v[0] to v[15].
They normally map to the vertex attributes. However, in the case of vertex state programs, v[0] is fed from LAUNCH_DATA (PGRAPH Methods 0x1E80, 0x1E84, 0x1E88, 0x1E8C for XYZW respectively) instead.
Output registers
11 output registers o[<RegName>] (initialized to XYZ=0x00000000 W=0x3F800000).
| Index | GL Name | D3D Name | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | HPOS | oPos | Homogeneous clip space position |
| 3 | COL0 | oD0 | Primary color (front-facing) |
| 4 | COL1 | oD1 | Secondary color (front-facing) |
| 5 | FOGC | oFog | Fog coordinate |
| 6 | PSIZ | oPts | Point size |
| 7 | BFC0 | oB0 | Back-facing primary color |
| 8 | BFC1 | oB1 | Back-facing secondary color |
| 9 | TEX0 | oT0 | Texture coordinate set 0 |
| 10 | TEX1 | oT1 | Texture coordinate set 1 |
| 11 | TEX2 | oT2 | Texture coordinate set 2 |
| 12 | TEX3 | oT3 | Texture coordinate set 3 |
Address register
A0.x exists as documented in the GL extension.
Temporary registers
There are 12 temporary registers: R0 to R11 (initialized to XYZW=0x00000000), as documented in the GL extension. Additionally, o[HPOS] is mirrored as R12 and can be used as source operand; so effectively you have 13 temporaries
Constant space
There are 192 constant registers in two seperate blocks with 96 constants each. They can be accessed through the PGRAPH RDI: select=0x17. Each constant slot is 4x DWORD, ordered as WZYX. Alternatively they can be uploaded through PGRAPH method [FIXME], with 4x DWORD, ordered XYZW.
In nvidia vertex programs only 96 constants are normally accessible. Microsoft exposed the 96 additional constant registers in D3D shaders through c[-96] to c[-1]. This documentation uses the GL terminology instead and expose the new registers as c[96] to c[191]. This means c[0] to c[191] valid.
Instructions
In total, there are 136 instruction slots.
Each slot consists of 16 bytes, we consider those as 4 seperate little-endian DWORDS describing the operation. Word 0 is inused.
| Meaning | Word | Offset (bits) | Size (bits) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ILU Operation | 1 | 25 | 3 |
| MAC Operation | 1 | 21 | 4 |
| Constant index | 1 | 13 | 8 |
| Input index | 1 | 9 | 4 |
| Source 1 negate | 1 | 8 | 1 |
| Source 1 swizzle X | 1 | 6 | 2 |
| Source 1 swizzle Y | 1 | 4 | 2 |
| Source 1 swizzle Z | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Source 1 swizzle W | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Source 1 register | 2 | 28 | 4 |
| Source 1 mux | 2 | 26 | 2 |
| Source 2 negate | 2 | 25 | 1 |
| Source 2 swizzle X | 2 | 23 | 2 |
| Source 2 swizzle Y | 2 | 21 | 2 |
| Source 2 swizzle Z | 2 | 19 | 2 |
| Source 2 swizzle W | 2 | 17 | 2 |
| Source 2 register | 2 | 13 | 4 |
| Source 2 mux | 2 | 11 | 2 |
| Source 3 negate | 2 | 10 | 1 |
| Source 3 swizzle X | 2 | 8 | 2 |
| Source 3 swizzle Y | 2 | 6 | 2 |
| Source 3 swizzle Z | 2 | 4 | 2 |
| Source 3 swizzle W | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Source 3 register (Hi) | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Source 3 register (Lo) | 3 | 30 | 2 |
| Source 3 mux | 3 | 28 | 2 |
| Destination MAC mask | 3 | 24 | 4 |
| Destination temporary register | 3 | 20 | 4 |
| Destination ILU mask | 3 | 16 | 4 |
| Destination overall mask | 3 | 12 | 4 |
| Destination select | 3 | 11 | 1 |
| Destination output register | 3 | 3 | 8 |
| Destination mux | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| Relative constant addressing | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Final instruction marker (EOF) | 3 | 0 | 1 |
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | X |
| 1 | Y |
| 2 | Z |
| 3 | W |
Functional units
Inverse Logic Unit (ILU)
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | NOP |
| 1 | MOV |
| 2 | RCP |
| 3 | RCC |
| 4 | RSQ |
| 5 | EXP |
| 6 | LOG |
| 7 | LIT |
Multiply-Accumulate (MAC)
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | NOP |
| 1 | MOV |
| 2 | MUL |
| 3 | ADD |
| 4 | MAD |
| 5 | DP3 |
| 6 | DPH |
| 7 | DP4 |
| 8 | DST |
| 9 | MIN |
| 10 | MAX |
| 11 | SLT |
| 12 | SGE |
| 13 | ARL |